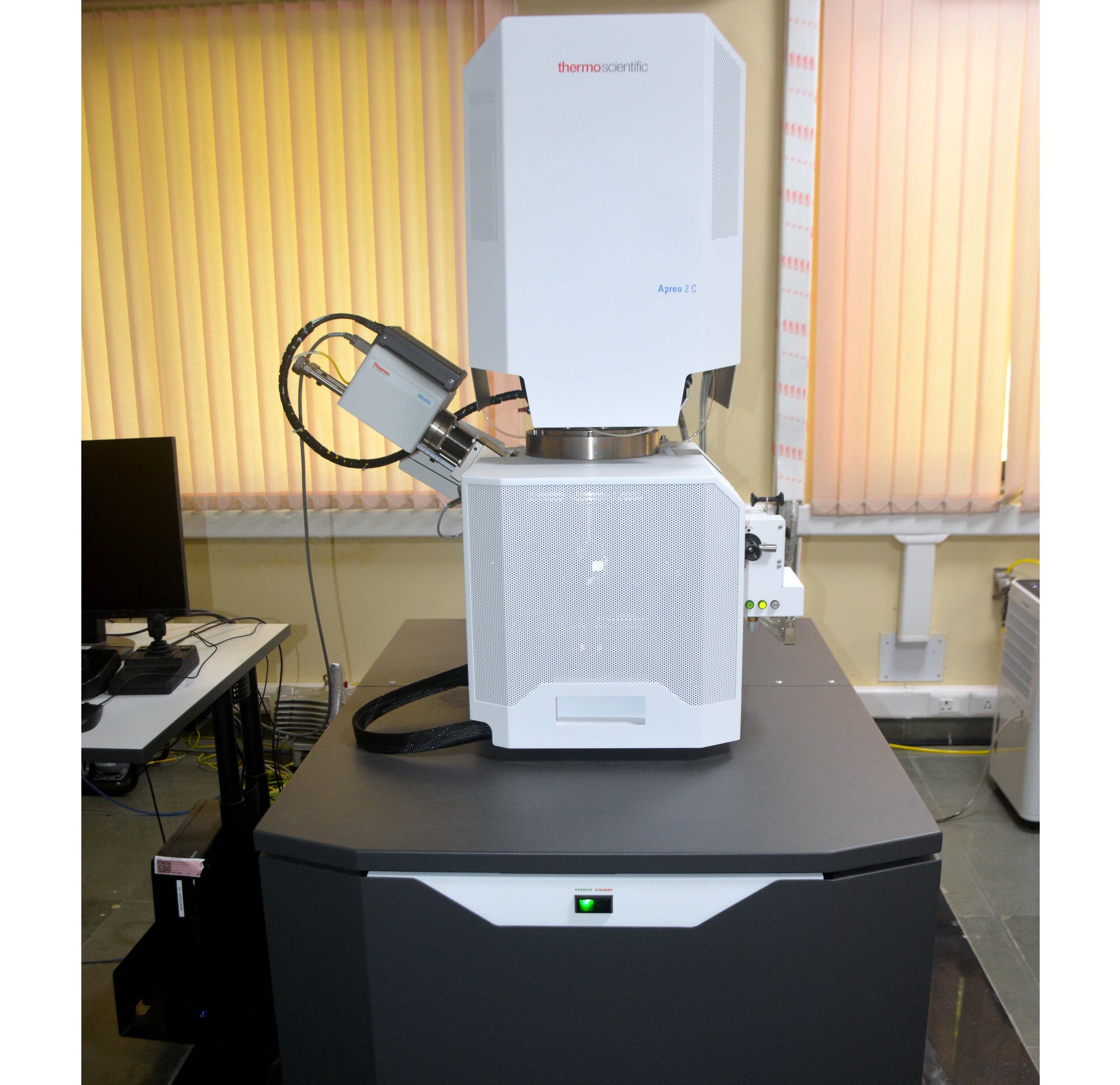
Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy (FESEM)- Thermo Fisher Scientific Apreo 2C
The FESEM (Thermo Fisher Scientific Apreo 2C) characterization facility provides high-resolution surface imaging and elemental analysis of a wide variety of materials. It utilizes a focused electron beam to scan a sample, generating signals-secondary electrons (SE), backscattered electrons (BSE), and X-rays-that reveal surface morphology, topography, and elemental composition.
FESEM is a crucial tool for research in materials science, nanoscience, and engineering, enabling the characterization of materials at the micro- and nanoscale. This instrument is equipped with ultra-high brightness cold field emission technology, allowing users to achieve sub-nanometer resolution and observe fine surface details at magnifications exceeding 1,000,000x.
With its advanced field emission gun and innovative beam path design, the Apreo 2C delivers superior resolution, contrast, and analytical performance, even at low accelerating voltages. It also supports live quantitative SEM image coloring using energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS), along with Point & ID, line scans, and elemental mapping.
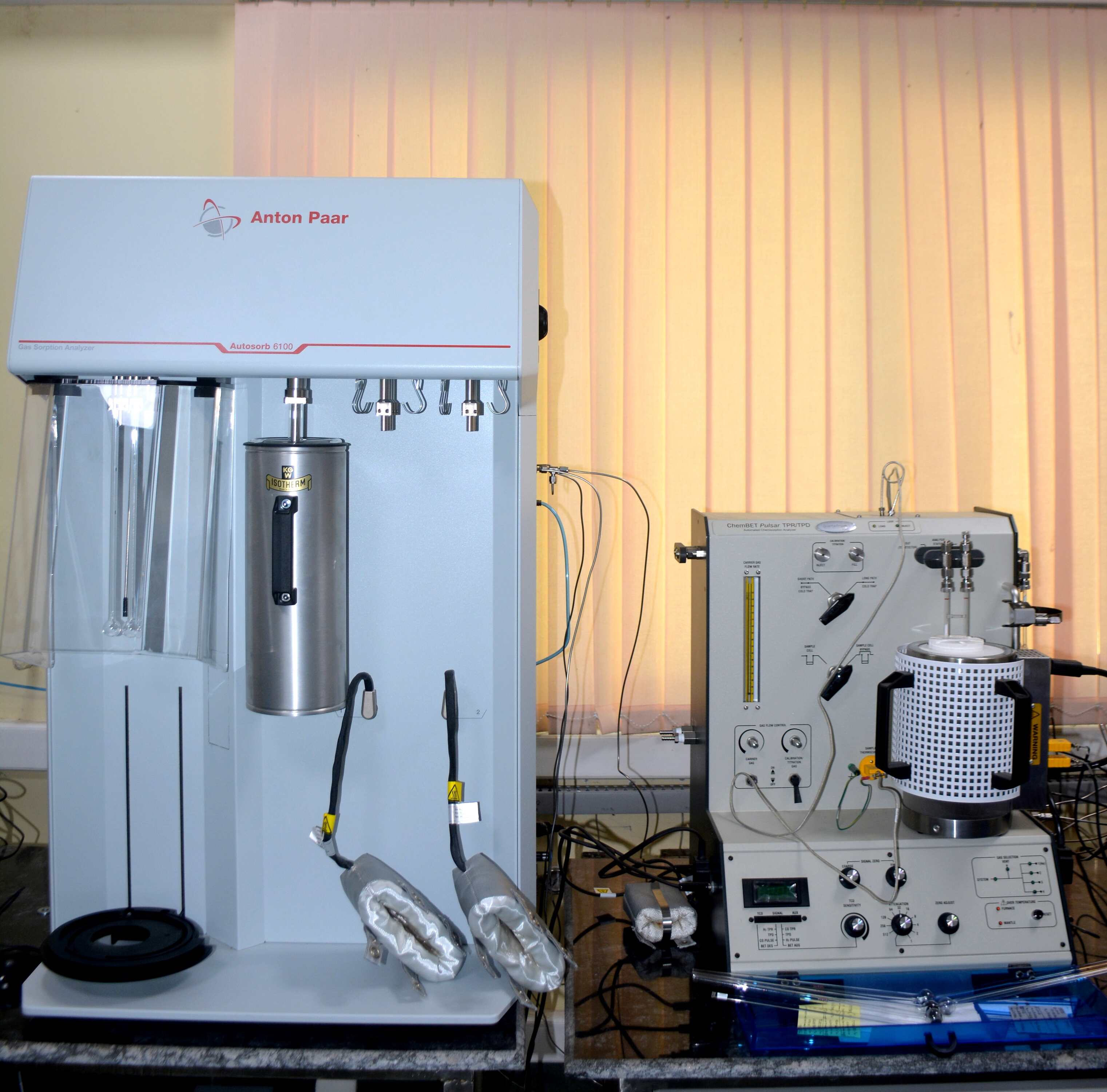
BET Surface Area Analyzer - Autosorb 6100
Autosorb 6100 is a high-resolution, automatic gas sorption analyzer used to determine the specific surface area, pore size distribution, and porosity of solid materials. The system operates based on the Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET) theory, which calculates the specific surface area by measuring the amount of gas adsorbed on the material's surface.
The system is equipped with three analysis ports, enabling up to three simultaneous sample measurements. Each port is fitted with 1000, 10, and 0.1 torr transducers, allowing accurate micropore and mesopore analysis at all ports. This instrument is widely used for characterizing powders, nanomaterials, catalysts, ceramics, porous solids, and composite materials, supporting research in materials science, chemical engineering, and environmental studies.
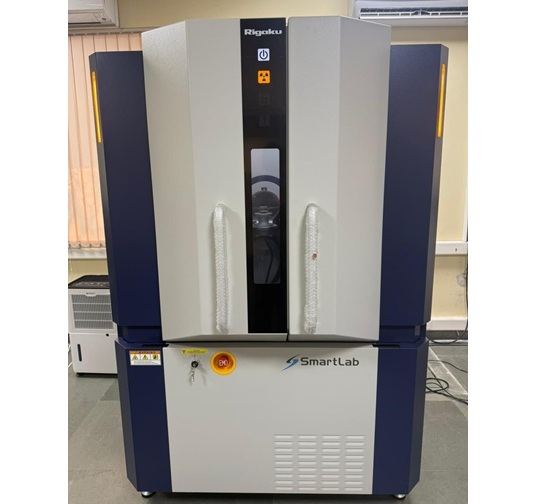


X-Ray Diffractometer (XRD) - Rigaku SmartLab SE
The Rigaku SmartLab SE is a versatile, fully automated, multipurpose X-ray diffractometer for structural characterization across a wide range of materials. It supports high-precision studies in powder diffraction, grazing-incidence thin-film analysis, and in-operando battery characterization.
Time-Resolved Photoluminescence (TRPL) Measurement System - PicoQuant: Fluotime 300 and Microtime 100
Time-Resolved Photoluminescence (TRPL) is a powerful technique used to investigate charge carrier dynamics, recombination mechanisms, and defect states in semiconductors, perovskites, quantum dots, and other optoelectronic materials. The TRPL setup includes a PicoQuant FluoTime 300 Photoluminescence Spectrometer coupled with a MicroTime 100 confocal microscope, operating on time-correlated single photon counting (TCSPC). The detection system consists of Hybrid PMA-07 photomultiplier tubes and Hamamatsu NIR-PMT detectors, supported by event timers (PicoHarp 300, HydraHarp 400, and TimeHarp 260).
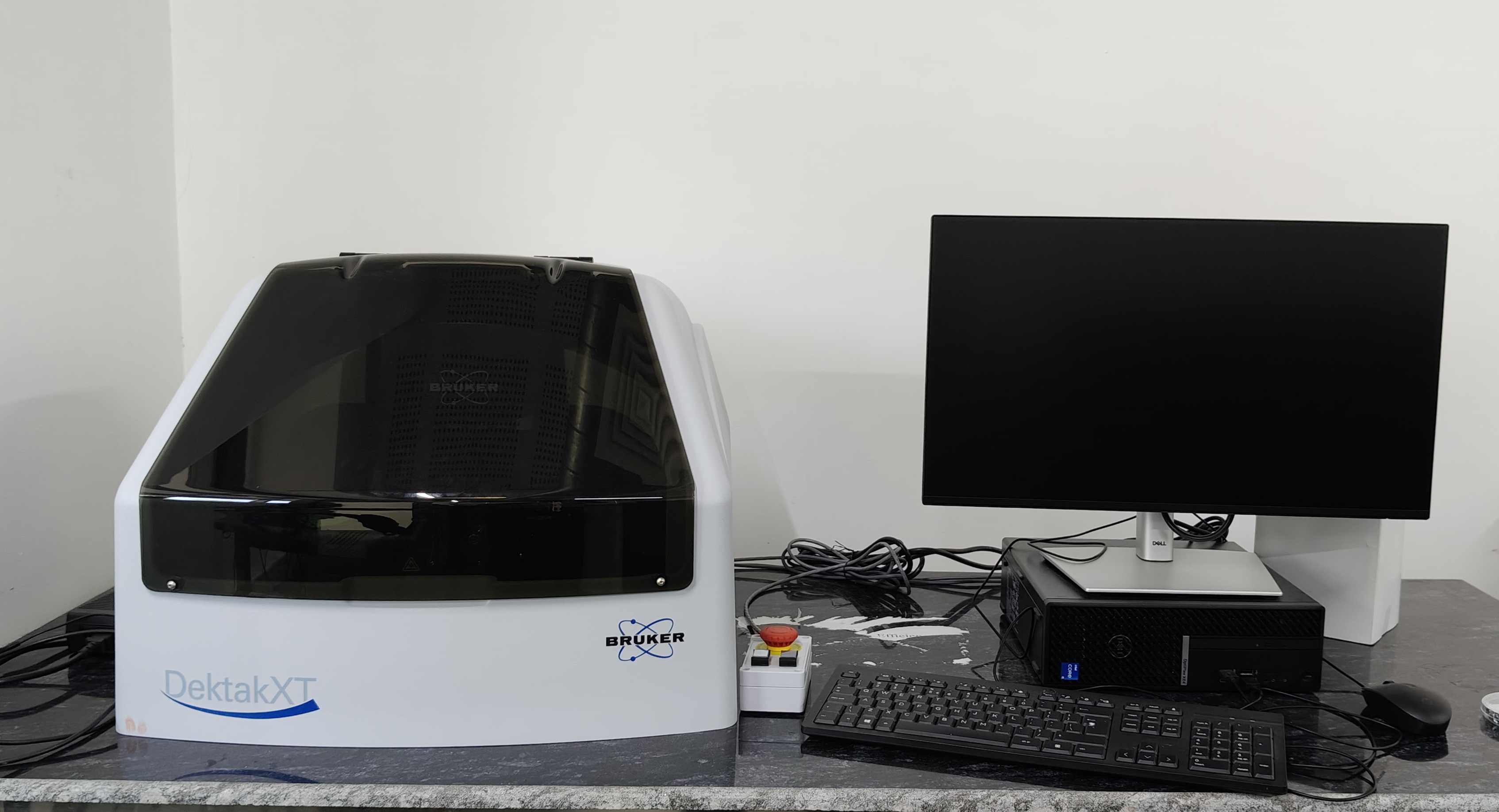
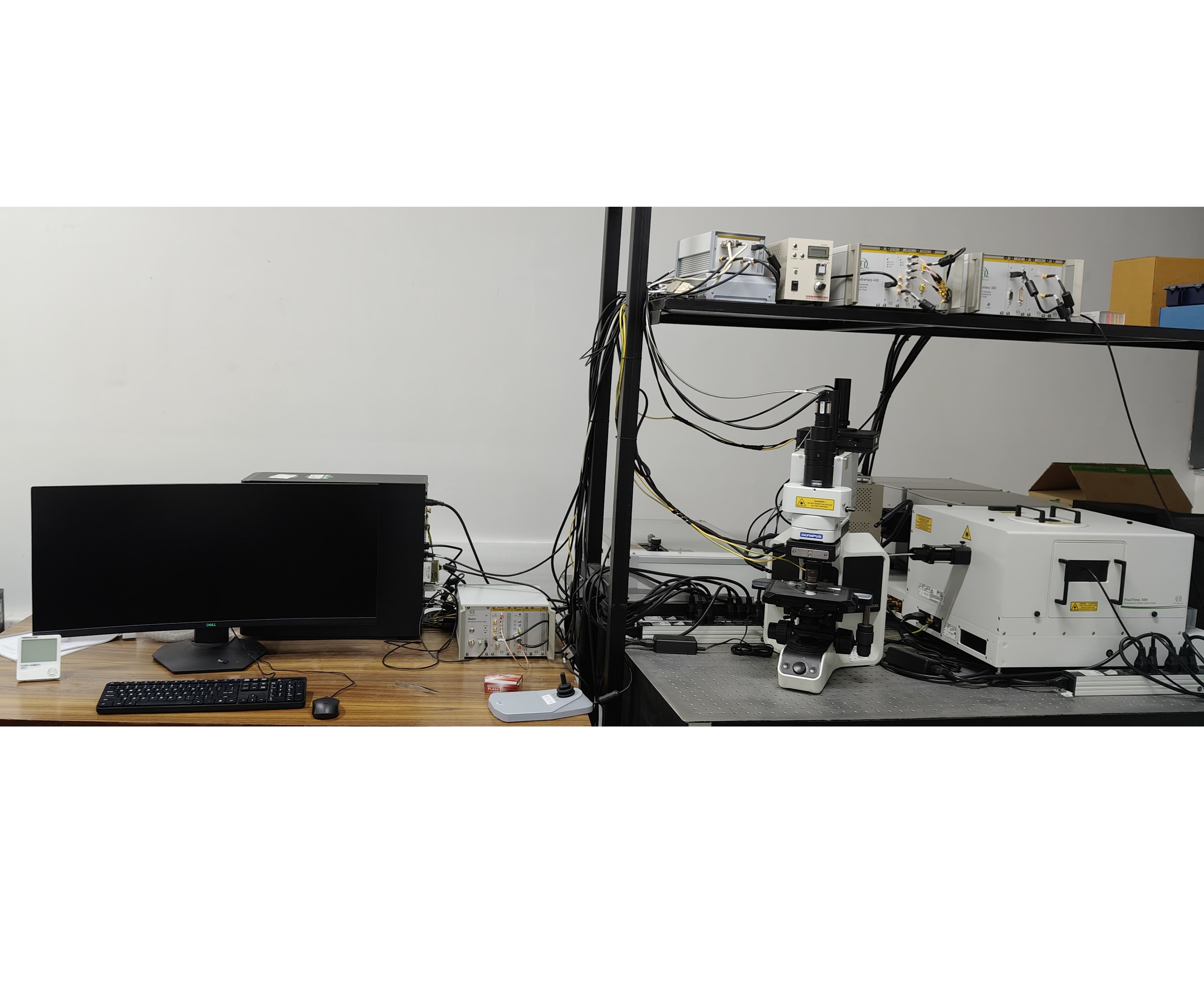

Stylus Profilometer-Bruker DektakXT
The Bruker DektakXT Stylus Profilometer is primarily used for measuring thin film thickness through physical contact using a pointed stylus tip. The stylus scans a surface with a step (etched or deposited), and the step height gives the film thickness. It offers precise measurements of step height and surface roughness, with a vertical resolution down to the angstrom level. The system supports a wide thickness range-from a few nanometers to over 100 microns.
UV-Visible Spectrophotometer - Agilent Cary 5000
The Cary 5000 UV-Vis spectrophotometer enables precise optical measurements across the ultraviolet, visible, and near-infrared regions. Its sample compartment is compatible with both thin-film holders and standard liquid cuvettes.
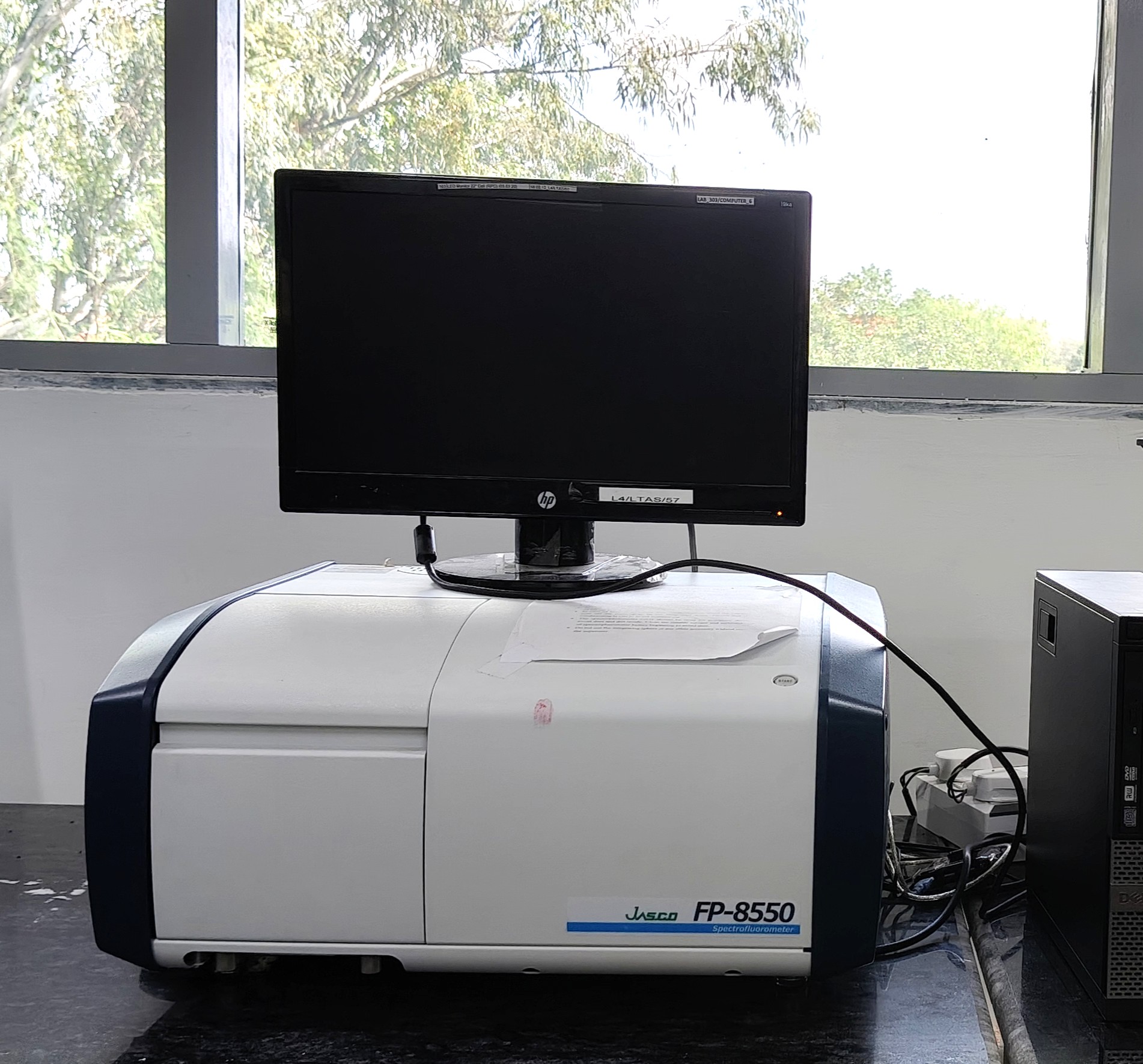


Photoluminescence Spectrometer - JASCO FP-8550
The JASCO FP-8550 is a high-sensitivity photoluminescence spectrometer designed for both qualitative and quantitative analysis of emission behavior across diverse materials.
Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectrometry (LCMS) System - Agilent 1260 Infinity II
The Agilent 1260 Infinity II LC/MSD is a high-performance liquid chromatography system integrated with a mass spectrometry detector, designed for fast and accurate purification and analysis of compounds from complex mixtures. It allows high-purity separations even for small sample amounts. The setup includes UV and MS detectors, multiple fraction collectors, and a quaternary pump for flexible solvent mixing. The system is ideal for compound purification, identification, and quantitative analysis in chemical, pharmaceutical, and materials research.
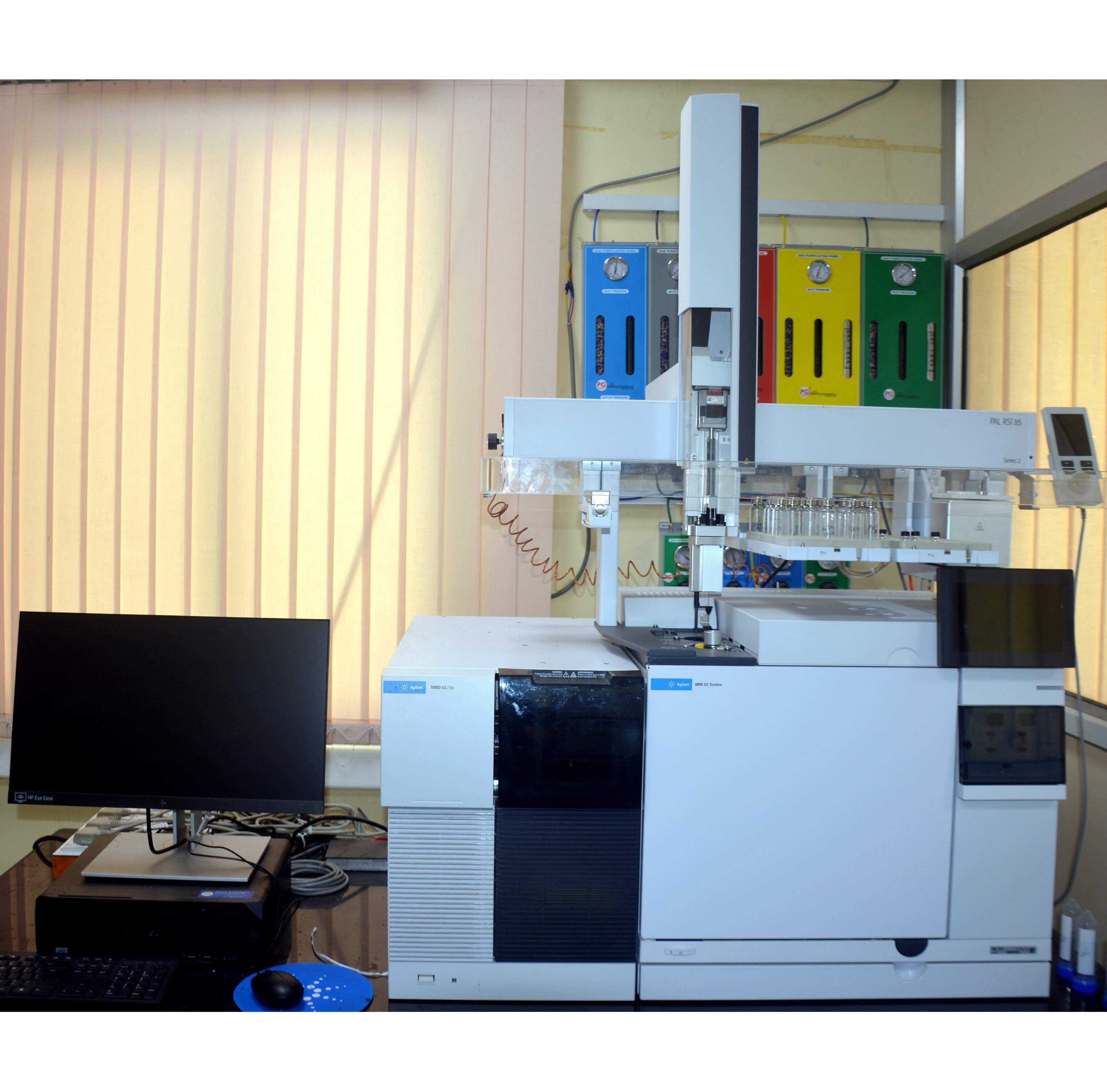
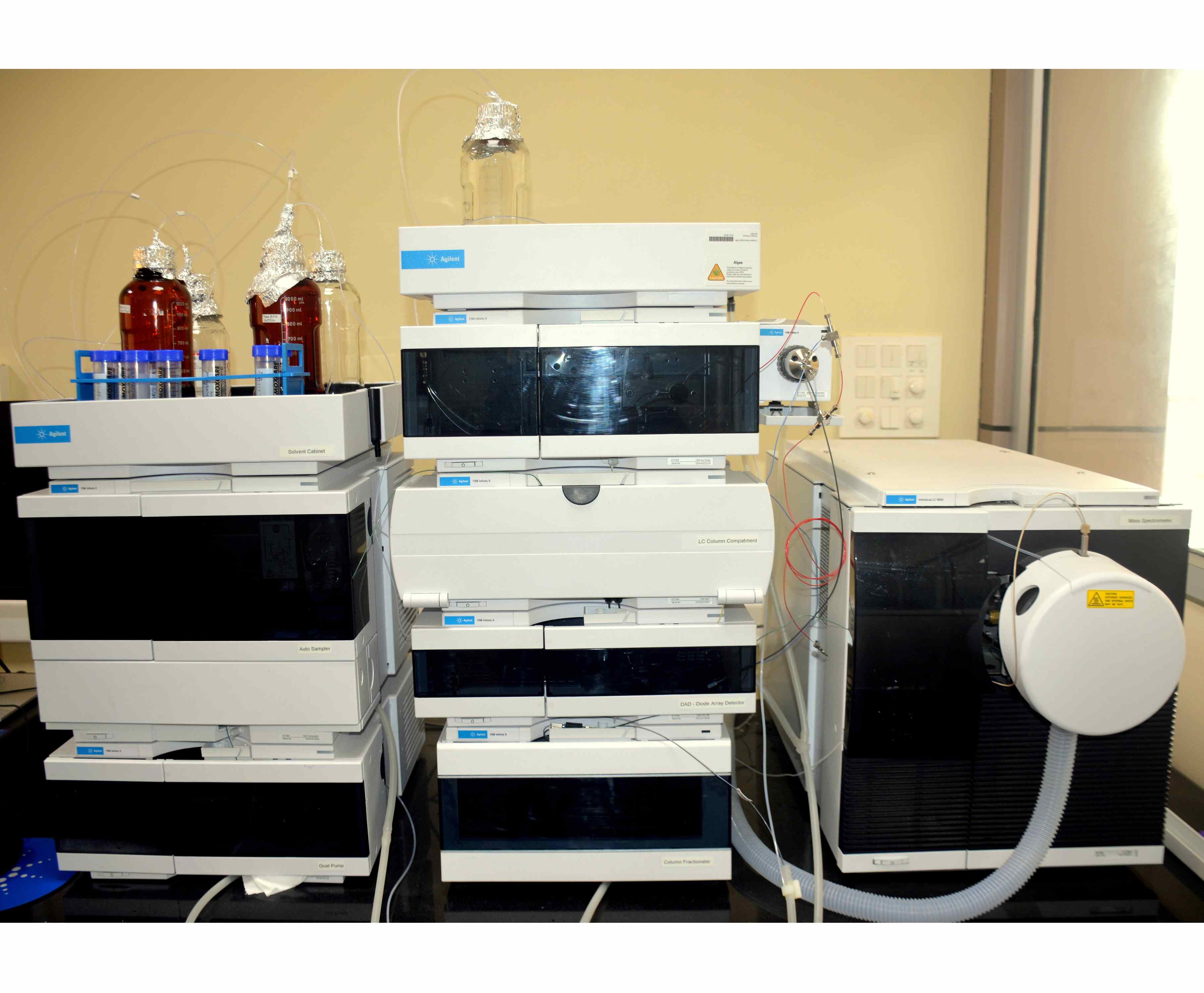

Gas Chromatography (GC) and GC-MS Systems - Agilent 8890 GC & Agilent 7010B Triple Quadrupole GC-MS
The Agilent 8890 Gas Chromatograph (GC) and Agilent 7010B Triple Quadrupole GC-MS System provide high-precision separation, identification, and quantification of volatile and semi-volatile compounds. The GC separates complex mixtures based on volatility and column interaction, while the MS detector provides detailed molecular information for compound identification, quantification, and structural analysis. Together, they deliver exceptional sensitivity, repeatability, and reliability for both routine and advanced analytical applications.
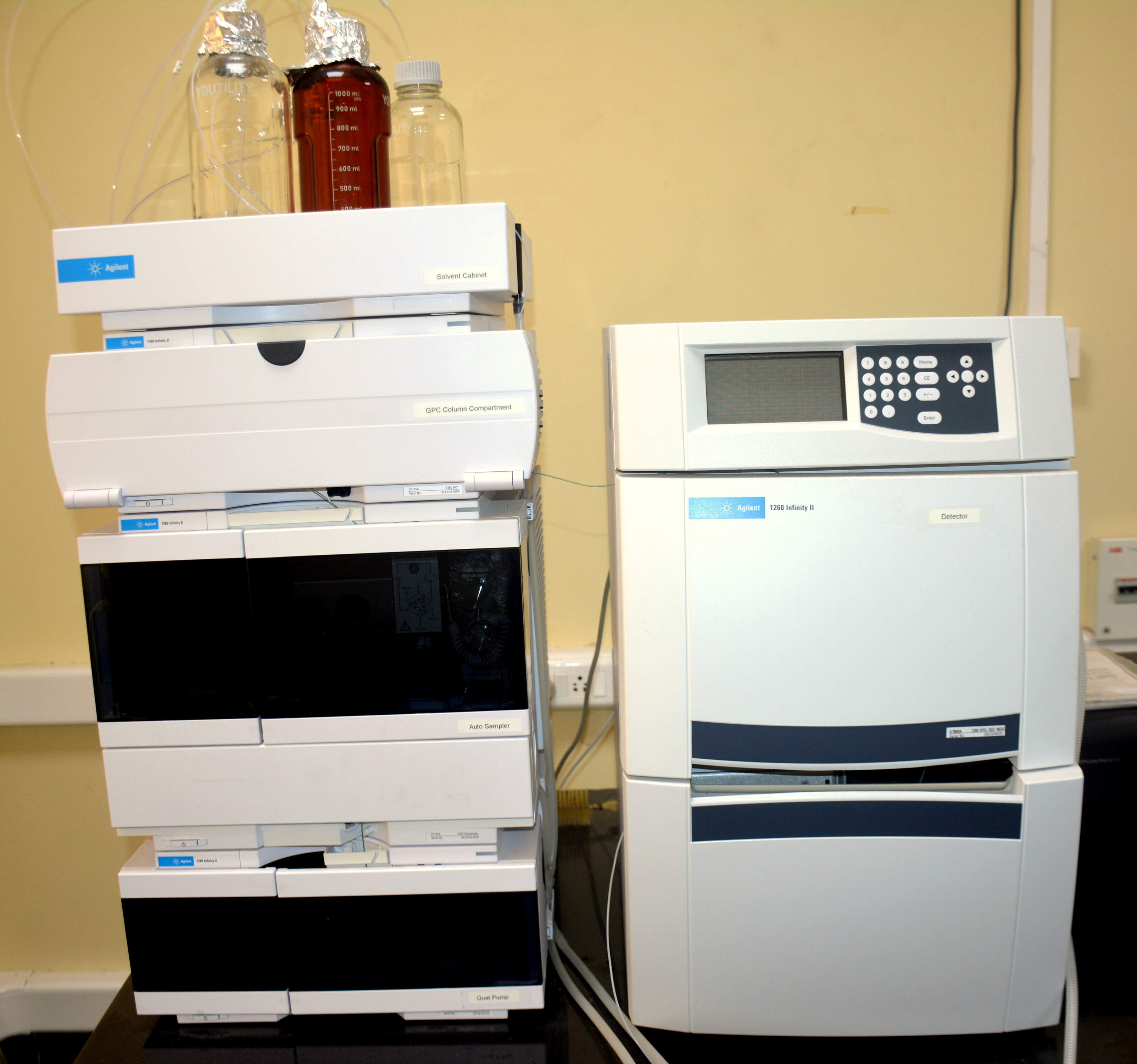
Gel Permeation Chromatography (GPC) System - Agilent 1260 Infinity
The Agilent 1260 Infinity GPC System enables precise molecular weight determination and polymer characterization. It provides accurate separation of polymers and macromolecules based on molecular size, offering insights into molecular weight distribution, viscosity, and branching. The system supports both organic and aqueous GPC applications with high reproducibility and temperature control.
