|
Syllabus: |
Introduction to I-D FEM Problems in structural mechanics using two dimensional elements. Plane stress, plane strain, axisymmetric analysis. Three dimensional stress analysis; Shell analysis. Solution of heat conduction, fluid flow, vibration, stability, and non-linear, large scale systems |
|
Credits: |
4 |
|
Syllabus: |
Structures and method of preparation of fibres and fibre reinforced composites. Micromechanics and prediction of elastic constants. Strength of composites. Properties of laminated composites and their constitutive |
|
Credits: |
4 |
|
Syllabus: |
ODE, matrix methods, root finding. Classification of PDE, finite differences, Steady and unsteady conduction, explicit and implicit method, advection- diffusion problems, upwinding, boundary-layers. Navier-Stokes equations, MAC and SIMPLE, finite element method for heat conduction |
|
Credits: |
4 |
|
Syllabus: |
Classical optimization methods, unconstrained minimization. Univariate, conjugate direction, gradient and variable metric methods, constrained minimization, Feasible direction and projections. Integer and Geometric programming, genetic algorithms, simulated annealing techniques, design applications. |
|
Credits: |
4 |
|
Syllabus: |
Fundamentals of solar radiation Review of fluid mechanics and heat transfer. Flat plate collectors, Focussing collectors, Solar water and air heating systems, solar cooling and dehumidification, solar energy storage, solar electric power, solar distillation of saline water and solar stills, solar cookers, solar pond and its thermal performance. |
|
Credits: |
4 |
|
Syllabus: |
Interaction devices and techniques, geometrical transformations, viewing in three dimensions, modelling and object hierarchy, raster algorithms, display, representation of 3-D shapes, rendering of surfaces and solids, hidden lines, edge and surface removal, shading models, shadows. |
|
Credits: |
5 |
|
Syllabus: |
Methodology of interactive, graphical, engineering design: Discretization, |
|
Credits: |
4 |
|
Syllabus: |
Project work involving the analysis, synthesis, material/component selection and detailed design of a mechanical system including the preparation of working drawings. The system may be integrated with electronics, electrical, hydraulic and other systems. Projects may be selected by students from any of the four streams, Fluid mechanics and Thermal sciences, Solid Mecahincs and Design, Manufacturing Science and Robotics. |
|
Credits: |
4 |
|
Syllabus: |
Fabrication of a prototype based on the work done in project-I. Qualitative |
|
Credits: |
2 |
|
Syllabus: |
Modeling, Analysis, and Simulation of Dynamic System; Mechanical, electronic, electrohydraulic and electomechanical systems; Stepper and Servo-motors; use of MATLAB; State-Space, laplace and frequency domain system behaviour; Bode, Nyquist, and root-locus plots; open and closed loop control systems; stability and sensitivity; PID, Phase lag and Phase lead compensation; Sampled data systems and Digtal controllers; DA/AD converters; Microprocessors; Sensors and actuators; interfacing with computers. |
|
Credits: |
4 |
|
Syllabus: |
Ergonomics-Estimation of performance and power requirements of Vehicles, Power Hydraulics, the form and function of Industrial Structures, product costing and pricing, the choice of suitable technologies, new engineering materials and their usage and costs. Case studies in engineering design, Industrial model making. Industrially sponsored project studies. |
|
Credits: |
4 |
|
Syllabus: |
Concepts and Practice: 2-D and 3-D form analysis in product design and in architecture; Aesthetics and Design; Evolution of design from craft to modern products; Technology and Society; Problem definition; Functional requirements, independence and hierarchy, constraints, non-uniqueness etc; Generation of ideas, courage, communication, decision making, synthesis and analysis. Robust design; Forms of traditional and modern societies - misfits between form and context, elimination of misfits, feedback. Studio Work : Design and fabrication of a product. |
|
Credits: |
4 |
|
Syllabus: |
Introduction to manufacturing system's concepts, manufacturing automation, flow lines and assembly systems. CAD/CAM; NC, CNC and DNC, adaptive control Manual and computer assisted part programming. Automated storage/retrieval systems; materials handling system including AGV; robot applications in manufacturing. Process planning, CAPP, scheduling and sequencing. GT and its benefits. Cost analysis, break even analysis and depreciation. Material management; inventory; MRP and MRP II; Just in time(JIT). Quality assurance and control; SQC, control charts; sampling; T.Q.M, Manufacturing system Simulation. FMS, CIMS, network and database for Mfg. system. |
|
Credits: |
4 |
|
Prerequisites: |
ME 361N |
|
Syllabus: |
General considerations in tool design. Work holding devices, design of jigs and fixtures. Design of press working tools. Blanking and piercing dies. Design of tooling for deep drawing. Design of limit guages |
|
Credits: |
4 |
|
Prerequisites: |
ME 253 & ME 362 |
|
Syllabus: |
Introductive to unconventional machining processes. Abrasive jet machining, ultrasonic machining, abrasive water jet machining, abrasive flow machining, water jet machining, electro chemical machining, electro discharge machining. Electron beam machining, laser beam machining and plasma arc machining. Design of tooling. |
|
Credits: |
4 |
|
Syllabus: |
Bond formation, properties of various moulding materials, principles of |
|
Credits: |
4 |
|
Prerequisites: |
ME 362 |
{slider= ME 471N — MECHANICAL ENGINEERING LAB}
|
Syllabus: |
Experimentation in automation and control, Solid Mechanics, Heat transfer, Energy conversion. |
|
Credits: |
4 |
|
Prerequisites: |
ME 301N, ME 321, ME 341, ME 453N |
|
Syllabus: |
Thermodynamic analysis of vapour-compression, air and non-conventional refrigeration systems, application and optimization of multistage and cascade refrigeration systems, refrigerants, fan pump, evaporator and condenser selection, Solar powered refrigeration, heat pump |
|
Credits: |
4 |
|
Syllabus: |
Moist air and psychrometric processes. Physiological principles of thermal comfort, calculation of cooling and heating loads; ADP determination, solar radiation and shading devices, duct design; Heat and mass transfer in air washers, cooling towers, finned heat exchangers; Air dehumidifi-cation. |
|
Credits: |
4 |
|
Syllabus: |
Turbomachine theory, potential flow to two dimensional cascades and experimental correlation, Conformal mapping and similarity methods. Methods for solving direct and inverse cascade problems for compressible flow, Axi-symmetric through flow, Advanced cycles, Stress analysis of components. |
|
Credits: |
4 |
|
Syllabus: |
The equations of motion in rotating coordinate system, effects of Coriolis and Centrifugal forces, energy equation, classification of turbomachines; two-dimensional cascade theory and experimental results; two dimensional flow analysis of axial impellers; three dimensional flow in axial turbomachines, radial equilibrium, secondary flows and loss estimation; off-design performance; radial and mixed flow machines; multistage axial compressors and turbines; prediction of stage performance and stacking; rotating stall and surge; turbine blade heat |
|
Credits: |
4 |
|
Syllabus: |
Analysis of stress and strain; Constitutive relationships; Failure theories; Torsion of non-circular sections. Plane stress and plane strain problems; Viscoelasticity, Structure and behaviour of polymers, behaviour of unidirectional composite and orthotropic lamina; Failure theories for fibre composites. |
|
Credits: |
4 |
|
Syllabus: |
Theory of constitutive equations with special emphasis on elasticity, plasticity and viscoelasticity. Solution of problems to illustrate effects of elasticity, thermo-elasticity, plasticity and viscoelasticity |
|
Credits: |
4 |
|
Syllabus: |
Analysis of stress and strain; Equilibrium, Compatibility and constitutive |
|
Credits: |
4 |
|
Syllabus: |
Introduction to I-D FEM. Problems in structural mechanics using two dimensional elements; Plane stress, plane strain, axisymmetric analysis; Three dimensional stress analysis; Shell analysis; Solution of heat conduction, fluid flow, vibration, stability, and non-linear, large scale systems. |
|
Credits: |
4 |
|
Syllabus: |
Review of single degree of freedom systems; Generalised coordinates, constraints, virtual work; Lagrange’s equation; Continuous systems; strings, beams; Raleigh-Ritz and Galerkin’s methods; Dynamics of rigid bodies in three dimensions; Euler angles; Euler’s equations of motion, Gyrodynamics. |
|
Credits: |
4 |
|
Syllabus: |
Vibration of discrete systems with single and multi degree of freedom. Hamilton’s principle, Langrange’s equations. Longitudinal vibration of bars, lateral vibration of straight and curved beams, vibration of membranes and plates, free and forced vibrations. Effect of damping. Wave motion in continuous systems. |
|
Credits: |
4 |
|
Syllabus: |
Phase space, singular points, limit cycle; Analytical methods, perturbation |
|
Credits: |
4 |
|
Syllabus: |
Introduction to probability theory, random processes, response of single, multi and infinite degrees of freedom systems to stationary random excitations. Failure due to random excitation. Brief discussion on measurement and processing of random data. |
|
Credits: |
4 |
|
Syllabus: |
ODE, matrix methods, root finding. Classification of PDE, finite differences, Steady and unsteady conduction, explicit and implicit method, advection- diffusion problems, upwinding, boundary-layers, Navier-Stokes equations, MAC and SIMPLE finite element method for heat conduction |
|
Credits: |
4 |
|
Syllabus: |
Stress-deformation relations, Navier-Stokes equation, exact solutions, two dimensional and axisymmetric boundary layers, Separation, Compressible boundary layers, Elements of stability theory, Turbulent flow: logarithmic law of the wall, effect of wall roughness, two and three equation models, fluid-solid interaction. |
|
Credits: |
4 |
|
Syllabus: |
Classification, characteristics, Euler’s equation, efficiencies, prerotation,vortex theory, methods to find the flow characteristics of a given runner geometry. Methods for finding plate profiles. Cavitation, prediction of cavitation inception, cavitation factor, similarity laws, NPSH, cavitation machines. |
|
Credits: |
4 |
|
Syllabus: |
Discretisation procedure in Finite-difference and Finite-volume. Navier-Stokes, Energy equations. Staggered rectilinear grids. Explicit methods : MAC, SMAC. Implicit Methods, SIMPLE and SIMPLER. Matrix methods, conjugate gradient method, strongly Implicit Procedure. Grid-Generation:Algebraic, Transfinite, Poisson equation methods. Finite-difference Navier-Stokes solution on non-orthogonal grids, transformation. Collocated grids. Finite-volume methods on non-orthogonal grids. Turbulence modelling, k-e modelling. |
|
Credits: |
4 |
|
Syllabus: |
Continuum, fluid deformation; Equations of continuity, momentum and energy, Navier-Stokes equations; Potential Theory: Blasius’ theorem, method of images. Linearized N-S equations, lubrication theory, creeping flows. Boundary layers, Momentum Integral and similarity techniques; Turbulence, Reynold’s equations, flow through pipes and over flat surfaces. |
|
Credits: |
4 |
|
Syllabus: |
One dimensional steady isentropic flow, normal and oblique shock; Fanno and Rayleigh lines. Prandtl-Mayer expansion. Isentropic flow in ducts, design of nozzles. Shock tube, small disturbance theory, flow past thin bodies, similarity rules. Hodograph plane, method of characteristics |
|
Credits: |
4 |
|
Syllabus: |
Velocity distribution function, B. element's equation, dynamics of collisions, standard molecular models, macroscopic equations, stress tensor and heat flux vector, slightly non-isentropic flow, dissipation coefficients, free molecular, near free molecular and near continuum flows, Couette flow, flow through tubes, S. Caption of B. element's equation. |
|
Credits: |
4 |
|
Syllabus: |
Modelling of wind turbine rotor blade, Uncoupled equations of motion for |
|
Credits: |
4 |
|
Syllabus: |
Governing equations. Extended surfaces, transient conditions. Convection in laminar and turbulent boundary layer and flow through tubes. Free and forced convection, correlations, Boiling and condensation. Heat exchangers. Radiation exchange between surfaces. |
|
Credits: |
4 |
|
Syllabus: |
Conduction: Steady and unsteady problems and their solutions in cartesian, cylindrical and spherical coordinates. Separation of variables. Duhamel’s theorem. Laplace transform. Problems involving change of phase. Inverse heat conduction, Microscale heat transfer, Radiation: Radiative exchange among black and grey and spectral surfaces, Shape factors. Applications to cavities and enclosures. Integral equations approach. Radiation from gases, vapours and flames. |
|
Credits: |
4 |
|
Syllabus: |
Conservation equations, boundary layers, free convection, forced convection. Heat transfer in laminar and turbulent, internal as well as external flows, mixed convection. Combined convection and radiation. Boiling and Condensation. Molecular diffusion in fluids, mass transfer coefficient. Simultaneous heat and mass transfer; Applications. |
|
Credits: |
4 |
|
Syllabus: |
Flame phenomena in pre-mixed combustible gases. Diffusion flames-analysis of single fuel droplet, chemical reactions. Burning in convective atmosphere, spray combustion, fire modelling, radiation in flames, formation and control of pollution, Combustion chambers. |
|
Credits: |
4 |
|
Syllabus: |
External flows, similarity, heat transfer from inclined surfaces, free convection flows, plumes, wakes, buoyant flows. Flow in stratified media. Stability of natural convection flows, transition, turbulent heat transfer correlations. |
|
Credits: |
4 |
|
Syllabus: |
Perturbation methods, transform methods, complex variables, eigen functions and series solution methods. Measurements of flow and temperature fields, optical methods, interpretation of data, design of experimental methods. Numerical method. |
|
Credits: |
4 |
|
Syllabus: |
Types of heat exchangers, definitions and quantitative relationships, analytical and numerical solution procedures. Thermal and hydraulic design of heat exchangers; Review of mechanical design, codes, materials for construction, corrosion damage, testing and inspection, costing |
|
Credits: |
4 |
|
Syllabus: |
Measure of turbulence, diffusivity, length scales. Reynolds equation. Mixing length models. Homogeneous, isotropic turbulence, correlation and energy spectrum functions, integral micro scales. Grid turbulence, jets, wakes and mixing layers, boundary layers, logarithmic-law near walls. |
|
Credits: |
4 |
|
Syllabus: |
Simulation of thermal processes, application to casting, extrusion, heat treatment, thermal design of heat exchangers, electronic circuitry. Optimization search method and geometric programming, control strategy, data storage and retrieval. Expert systems. |
|
Credits: |
4 |
|
Syllabus: |
Probes and transducers; Calibration; Turbulence measurement via statistical measures; Single and multi-point correlations; Signal conditioning; Optical methods, Interferometry, Schlieren, shadowgraph, LCT, Laser Doppler velocimeter; Transient and frequency response. Computer aided data acquisition, tomography. |
|
Credits: |
4 |
|
Syllabus: |
Introduction to the Solar System, The 2- and restricted 3- body problem; |
|
Credits: |
4 |
|
Syllabus: |
Kinematic elements and pairs, mechanisms with lower and higher pairs, geometry of motion, type number and dimensional synthesis of mechanisms, analytical and graphical methods of analysis and synthesis of linkages, Coupler curve synthesis, spatial mechanisms, cams and gears |
|
Credits: |
4 |
|
Syllabus: |
Review of kinematics and kinetics of a particle and a rigid body in plane motion. Euler’s equations; Methods of analytical dynamics, Lagranges equations; Hamilton’s principle; Dynamics in phase space and introduction to stability theory; Applications to engineering problems. |
|
Credits: |
4 |
|
Syllabus: |
Kinematics and dynamics of rigid bodies and system of rigid bodies. Dynamic force and motion analysis of mechanisms and machines with rigid links. Elastodynamics and kineto-elastodynamic analysis of mechanisms with flexible members. Balancing of linkages. |
|
Credits: |
4 |
|
Syllabus: |
Simple dynamical models of ground vehicles, mechanics of pneumatic tires, mechanics of vehicles-terrain interaction, performance characteristics of road vehicles, Handling characteristics. Directional stability, wheel shimmy, vehicle ride characteristics. |
|
Credits: |
4 |
|
Syllabus: |
Interaction devices and techniques, geo-metrical transformations, viewing in three dimensions, modelling and object hierarchy, raster algorithms, display, representation of 3-D shapes, rendering of surfaces and solids, hidden lines, edge and surface removal, shading models, shadows. |
|
Credits: |
4 |
|
Syllabus: |
Vector functions, reference frames, derivatives of vector functions. Kinematics. Mass/Inertia distribution. Generalized forces and energy functions. Formulation of equations of motion. Linearization and integrals of equations of motion. Extraction of information from equations of motion. Computational issues. Dynamics of a combination of rigid and flexible bodies. |
|
Credits: |
4 |
|
Syllabus: |
Linear and Rotary actuators, valves and their characteristics. Flow forces on valve spools, valve design, control actuators. Hydraulic power packs, torque motor, electrohydraulic valves, FES, DPF, SLEW servovalves, Electrohydraulic servo systems; Pneumatic control elements; Pneumatic servo systems. |
|
Credits: |
4 |
|
Syllabus: |
Basic principle of numerical control, Classification of NC systems,. NC part programming-manual and computer aided. Drives, feedback devices, Counting devices used in NC system. Interpolators for Manufacturing system. Control loops for NC system, Adaptive control, Industrial robots |
|
Credits: |
4 |
|
Syllabus: |
Geometric modelling, intrinsic and parametric representations, differential |
|
Credits: |
4 |
|
Syllabus: |
Mechanics of chip formation, chip curl. Bluntness and cutting forces. Thermal aspects of machining. Tool wear, tool life and economics of machining. Mechanics of grinding, forces and specific energy, temperature. wheel wear and surface finish. |
|
Credits: |
4 |
|
Syllabus: |
General classification of unconventional machining, chemical machining, electric discharge machining, Abrasive Jet and Ultrasonic Machining, electron beam machining, laser beam machining, ion beam machining, plasma arc machining; Comparative evaluation of different processes; Conventional machining with modifications. |
|
Credits: |
4 |
|
Syllabus: |
Fundmentals of plasticity, yield and flow, anisotropy, instability, limit analysis, slipline field theory. Applications to forging, wire and tube drawing, deep drawing, extrusion and rolling. High velocity forming. |
|
Credits: |
4 |
|
Syllabus: |
Considerations in designing spindle bearing. Functions of guides and slide ways. Static and dynamic analysis of m/c tool structures. Control and automation of m/c tools. Special topics. |
|
Credits: |
4 |
|
Syllabus: |
Forced vibrations; Machine tool chatter, dynamics of metal cutting; Chatter in some typical machine tools; Effect of flexible mounting on chatter; Chatter in coupled machine tool systems; Theory of chatter with several degrees of freedom; Theory of impact dampers; Dynamics of machine tool structures |
|
Credits: |
4 |
|
Syllabus: |
Strain Gauge, strain rosettes and transducer applications. Photoelasticity, |
|
Credits: |
4 |
|
Syllabus: |
Photoelasticity. Stress-optic law. Photoelastic coatings Strain-optic law, photoelastic materials. Role of Digital Image processing techniques for automation. Strain gauges, Rosette analysis, Transducers, Case studies. Introduction to Brittle coatings, Moire, Holography, Speckle and Caustics. |
|
Credits: |
4 |
|
Syllabus: |
Properties of Vector Algebra, Vector space, subspace, basis, null and range space, invertibility and matrix representation; Cartesian Tensor notation and vector analysis; Matrices and Matrix algebra, Echelon form, orthogonalization; Eigen values and eigenvectors of a linear operator; First and second order ODEs, Linear Differential equations with constant coefficients and equidimensional equations; Second order linear homogenous differential equations and their solutions; Methods of Taylor and Frobenius, Laplace and Fourier transforms, Fourier series; Legendre and Bessel functions; Sturm Louville Problem; classification of PDEs; |
|
Credits: |
4 |
|
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
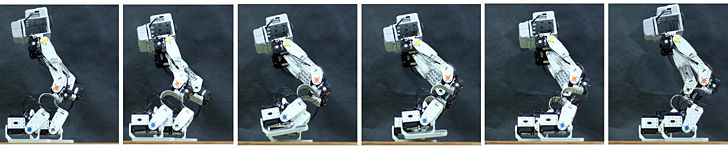
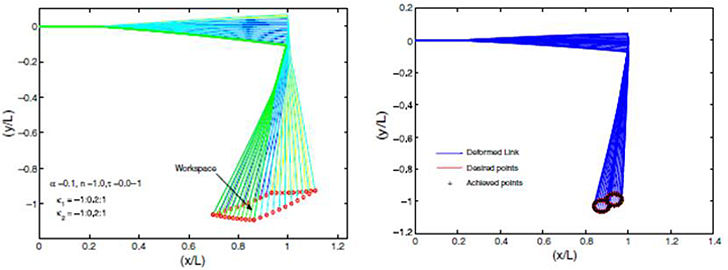
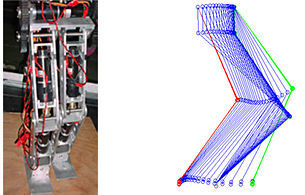
Compliant and Robotics Systems (CARS) Lab |
Compliant Mechanisms and Robotic Systems
|
|
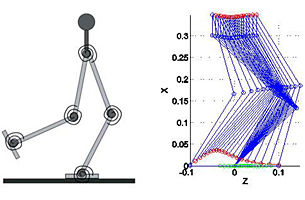
Robotics Lab |
|
|
Smart Materials, Structures & Systems Laboratory |
3D Laser Doppler Vibrometer, dSpace ACE 1103, 1104, Multi channel SMA amplifiers, d33 meter, Magnetic Levitation Control |