- Publications
- Centers & Facilities
- Centers
- Advanced Center for Material Science
- Center for Environmental Science & Engineering
- Advance Center for Electronic System
- National Information Center of Earthquake Engineering
- BSNL-IITK Telecom Center of Excellence
- SAMTEL Center for Display Technology
- Center for Mechatronics
- Syndicate Bank Entrepreneurship Research & Training
- Center for Laser Technology
- Thematic Unit of Excellence
- Facilities
- Centers
- Innovation & Incubation
- Initiatives
- Industry Collaborations
- DORD Office
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Department of Aerospace Engineering
Name of the PI- Prof. Sanjay Mittal Duration- 1-2 days Abstract- Introduction to the method of weighted residuals; Comparison of various methods; Application of the Galerkin Method to a simple 1D boundary value problem; Generalization to a 2d/3D problem with examples from heat conduction/fluid dynamics; Shape functions; Programming Concepts; Unsteady problems; Handling Non-linearity,; Finite Element Methods for Compressible and Incompressible Flows; High Performance Computing; Fluid-Structure Interactions; Case studies.
Name of the PI- Prof. Sanjay Mittal Duration- 1-2 days Abstract- The continuum hypothesis; Eulerian and Lagrangian frames; Steady and unsteady flows; Governing Equations; Potential Flows; Boundary Layer; Similarity Laws; Flow over airfoils; Flow over wings; Turbulent v/s Laminar Flows; Stability and Transition; Certain Flow Examples.
Name of the PI- Prof. Sanjay Mittal Duration- 1-2 days Abstract- Basic Fluid mechanics; Bluff body flows; Basic Structural Mechanics; Numerical Methods for Fluid Mechanics; Numerical methods for Structural Mechanics; Computational challenges in Fluid-Structure interactions; Consistent transfer of information between fluids and structures modules; Lock-in/Synchronization; Added Mass; Effect of flexibility and mass-ratio; Control Strategies; Case studies.
Name of the PI- Prof. G.M. Kamath Duration- 8 to 10 days Abstract- This course is designed to provide a practical in-flight exposure and demonstration of some of the principles of aircraft flight mechanics, performance, stability and control in conjunction with the requisite theoretical background. The course contents include: introduction to aircraft instrumentation and calibration; estimation and evaluation of aircraft drag characteristics, cruise & climb performance parameters; determination of stability and control characteristics; observations of airplane dynamic modes. The course could be customized to include specific topics of interest within the gamut of the areas aforementioned.
Department of Biological Sciences & Bioengineering
Name of the PI- Prof. Arun K. Shukla Duration- 3-5 days Abstract:G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) represent the largest class of cell surface receptors in the human genome and they are involved in almost every physiological process in our body. GPCRs are targeted by approximately half of the currently prescribed medicines such as beta-blockers for heart failure, angiotensin receptor blockers for hypertension and histamine receptor blockers for allergy. Discovery of new signaling and regulatory paradigms of GPCRs offers unique untapped territories for novel therapeutics with minimal side-effects, and it is changing the landscape of drug-discovery in major pharmaceutical ventures. This course essentially aims to cover the fundamentals of GPCR biology and emerging concepts with particular emphasis on previously uncharted avenues for more specific and effective drugs.
Name of the PI- Prof. Arun K. Shukla Duration- 3-5 days Abstract:Antibodies are one of the most important reagents in any biology laboratory across the world. Still however, the quality, reliability and cost of commercially available antibodies generated through conventional immunization and hybridoma based approaches have been a major issue, and many a times, it poses a significant hurdle in advancing the biological research. This course aims to familiarize the audience with rapidly emerging Synthetic Antibody Technology Platforms, and provide a deep understanding of alternative solutions to major challenges encountered in antibody discovery and development. This course also covers the details of non-antibody based synthetic and designer proteins with specific case-examples, and how these can be utilized in biochemical, cell-biological and therapeutic applications.
Department of Computer Science & Engineering
Name of the PI: Prof. Amey Karkare Duration- 2 to 7 days
Name of the PI- Prof. Arnab Bhattacharya Duration- 5 to 7 days Abstract- With the massive increase in available datasets across different domains such as social networks, traffic data, images, biological and chemical compounds, streaming web-clicks, etc., the role of data processing is becoming even more important. Traditional relational databases enforce consistency constraints and are, therefore, not always suitable and efficient for applications that do not require such stringent constraints. Consequently, the use of "big data" technologies (technically also known as NoSQL databases) have proliferated. They do not require structured tables and are, therefore, more suitable for handling free-form unstructured or semi-structured data such as text, images, graphs, etc. Since the focus is more on efficient updates and retrievals, the big data architecture naturally allows for parallel processing. This course will cover the basics of big data processing and the associated tools and techniques for them.
Department of Civil Engineering
Name of the PI- Prof. Animesh Das Duration- 3 to 4 days
Name of the PI- Prof. Animesh Das Duration- 3 to 4 days Abstract- The need for good transportation engineers, equipped with the knowledge of modern as well as traditional techniques, cannot be overstated. It is, in this context, that the short course on "Principles of Transportation Engineering" covering modern techniques, without overlooking the traditional methods, is designed. The course promises considerable value addition to the industry personnel as well as college/ university teachers. The course emphasizes the theoretical principles of Transportation Engineering and design.
Name of the PI- Prof. Priyanka Ghosh Duration- 5 days Abstract- Soil dynamics is the branch of geotechnical engineering that deals with the behaviour of soils and rocks under dynamic loads by several sources such as earthquakes, blasting, operation of machinery, construction operations, mining, traffic, wind and wave actions. This course will prepare the participants with the advanced knowledge developed recently in understanding the response of soil and rock subjected to various types of dynamic or cyclic time-dependent loading conditions. This advanced course material will be very useful for researchers, teachers, scientists and practitioners.
Name of the PI- Prof. Nihar Ranjan Patra Duration- 5 days Abstract- The term ground improvement and ground modification refer to the improvement in or modification to the Engineering properties of a soil that carried out at a site where the soil in the natural state doesn't possess properties that are acceptable to us for the proposed civil Engineering activities. The improved or modified soil exhibits satisfactory performance when foundations, earth structures, earth retaining structures and under ground structures are constructed on, within or using the soil.
Name of the PI- Prof. N. R. Patra Duration- 5 Days Abstract- Applications of soil mechanics such as earth retaining structures, slope stability analysis, etc. to design various Geotechnical Structures.
Name of the PI- Prof. Tarun Gupta Duration- 1-3 days Abstract- Day by day increase in pollution load in the ambient air has lead to invention and innovation in technology and tools for aerosol and gas measurement. Keeping the needs of industry and research institutes this course will cover the basics of instrument principles, design, fabrication and their application to various outdoor as well as indoor microenvironments. The accuracy and limitations and applicability of both integrated and real-time instruments will be discussed.
Name of the PI- Prof. Tarun Gupta Duration- 1-2 Days Abstract- This course will discuss the various interaction and chemistry between tropospheric photochemical species like oxides of nitrogen, volatile organic compounds and ozone. The idea is to understand the basic of photochemical reactions and how the emissions from either natural sources or industrial sources tilt the equilibrium and results in what kind of key chemical species either in gas phase or their eventual conversion to particulate phase. Brief introduction to secondary organic aerosol (SOA) will also be made.
Name of the PI- Prof. Tarun gupta Duration- 1–3 Days Abstract- This course will provide stepwise information about role of fuel, lubricating oil and engine technology in the kind of pollutant (gaseous as well as particles) being formed inside the combustion chamber and their physico-chemical transformation including partial oxidation by the time they exit the tail-pipe. Both integrated and real-time measurement devices used for exhaust measurement and characterization will be covered. In addition, various in-cylinder as well as after-treatment control devices relevant to internal combustion engine applications will be discussed in detail.
Department of Physics
Name of the PI- Prof. Krishnacharya Duration- 5 − 7 days Target Industries: Materials, Polymer, Paint, Adhesive, Textile, Coating industries Abstract- The course will cover various fundamental and applications of Surface and Interfacial Engineering phenomenon. The course will start with an initial discussion on thermodynamic aspect of various intermolecular forces. Then understanding about different surface forces and energies e.g. ionic, covalent, hydrogen, van der Waals etc. will be established. This understand about surface forces will provide necessary background to explore surface engineering. Subsequently various surface phenomenon e.g. wetting, slip, adhesion, friction to name a few will discussed in details. Fundamentals as well as applications of all surface phenomenon will be explored. Towards the end, application and engineering of all surface phenomenon will be discussed. Various examples taken from our daily life will be used to understand the impact and importance of the proposed topic.
Figure: Optical image of a polyester textile showing almost spherical shape drops of water and silicone oil depicting omniphobic behavior after a suitable oleophobic coating.
Design Programme
Name of the PI- Prof. Jhumkee Sengupta Iyengar Duration- 2 days Abstract- Today there is a lot being spoken and written about Design Thinking. It has not just gotten the attention of industry leaders but has reached the center stage in many organizations that are trying to rapidly adopt a PEOPLE CENTERED approach and culture in order to be more INNOVATIVE. Design Thinking is enabling organizations to create products and services that are not just what people want but are also differentiators in the market. This hands-on course, will also help you understand how a People Centered Design approach is different from traditional engineering or marketing focused approaches and understand as well how you create designs that are focused on the people who will use them through a design challenge. Professionals from various industries and levels of experience can learn these approaches and the associated methods, concepts and tools. These methods and approaches are versatile and they adapt well to various industries, settings and projects. They will equip you with the Understanding and Appreciation of a different way of thinking and looking at the world and help you to approach a problem in a way that makes the outcome a lot more Innovative - not innovative for the sake of innovative, but INNOVATIVE in the SERVICE of PEOPLE.
Department of Industrial & Management Engineering
Name of the PI- Prof. Raghu Nandan Sengupta Duration- 5 days Abstract- Total Quality Management (TQM) is the study of the principles which concerns an organization, whether manufacturing, services or government, to deliver high-quality products/services to its customers by maintaining high standards of work in every aspect of the organization's/company's operations. TQM involves the in-depth analysis of qualitative, quantitative as well as philosophical aspects of an organization, and as such the course would have an enhanced rigour and emphasis in learning the tools of quality control, statistical process control, control charts, design of experiment, etc. After attending this course engineers/managers/decision makers would definitely be better equipped to handle issues related to quality control and how to effectively use TQM in all spheres of the organization's progress.
Name of the PI- Prof. Raghu Nandan Sengupta Abstract- The focus of this course, is to equip the participants with the concepts and necessary tools in probability & statistics which have a variety of applications in different areas of common interest. The course will start with a thorough understanding of the concept of probability and conditional probability. After that the focus will be on the concepts of random variables, expected value, variance, etc. Apart from understanding the whole gamut of discrete as well as continuous distributions, the course will also emphasize the importance of joint distributions and their unique practical uses. Later on the course will cover sampling distribution, inference techniques and highlight how these methods are used in a variety of application areas like engineering, management science, etc. In the final part of the course we will get an in-depth understanding of what analysis of variance is along with a thorough understanding of the concepts of simple linear regression.
Name of the PI- Prof. Raghu Nandan Sengupta Abstract- The course is designed to guide the participants along the difficult terrain of quantitative finance (QF), make them aware of different mathematical tools used in QF, equip then with the necessary skills for financial risk management, apprise them about the nuances of algorithmic design, and other such related issues, etc. The course is designed to support the participants exploration and learning of various theories in the area of risk management. Participants after completing this course will appreciate how different metrics like variance, VaR, CVaR, etc., are used to measure risk. Apart from that they would also study and understand how EVD and concepts of copula theory is used along with different tools of optimization to study a variety of risk management techniques. Furthermore issues related to different credit rating measures like Z-Score, ZETA-Score, O-Score will also be covered, apart from covering interesting topics related to swaps, derivative pricing, etc.
Name of the PI- Prof. Raghu Nandan Sengupta Abstract- Data Analysis & Operations Research is the scientific process of transforming data into meaningful use such that the insights gained enables us in making enhanced and prudent decisions. This course is a synergistic use of knowledge to understand concepts of modeling and analysis in the area of Big data usage from both theoretical as well as practical point of view. Use of different Linear Programming (LP), Non-Linear Programming (NLP), MILP programming, Goal Programming, etc., will be the first set of emphasis in this course. Next we will cover simple ideas in the area of utility theory to help us understand MCDM and MODM. The course will also cover ideas and applications of different non-parametric techniques like Data envelopment analysis (DEA), Analytical Hierarchy Process (AHP), Analytical Network Process (ANP), TOPSIS, ELECTRE, Regression/Logistic regression, classification & clustering tech-niques, Support vector machines (SVMs), Bayesian Models, Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) methods, and such related topics.
Name of the PI- Prof. Amit Shukla Abstract- Staffing is one of the most critical activities of the HRM process, as a right or wrong decision can make a difference between success and failure. This short term program aims at helping organizations undertake this process by deploying both top down (strategic staffing) and bottom-up (aligning internal and external factors) approaches: so as to render the process highly effective. The study material will be eclectic in nature so as to provide a modern and variegated outlook. Further, the contents will be customized according to the organizational needs. Topics covered will be as follows: Job Analysis Techniques, Competency Based Staffing, Competency Mapping, Decisions Regarding Selection Tools, Training Needs for Internal Recruiters, Induction and Deployment.
Name of the PI- Prof. Amit Shukla Abstract- Stress is an integral part of modern work life. This short term program aims to put in perspective various aspects of stress, its impact, and management techniques. The study material will be eclectic in nature so as to provide a modern and variegated outlook. Further, the contents will be customized according to the organizational needs. Topics covered will be as follows: Modern Outlook on Stress, Types of Stress, Effects-Both Positive and Negative, Self Knowledge, Role of Work Life Balance, Mitigation/Management Techniques.
Name of the PI- Prof. RRK Sharma Abstract- Introduction to MRP systems; two multi pass heuristics (lot size modification and the lead time time modification) to improve performance; a multi pass heuristic that seeks to achieve better co-ordinated arrivals at assembly centers which has impressive performance; a multi pass heuristic that seeks to modify the schedules in successive iterations, Chapter 5 gives more computational experience on the performance of heuristic that modifies the lot sizes; a combination heuristic that performs well when there is high variation in machine capacity utilization, good heuristics for the case of pure assembly MRP systems; heuristic that lets schedules of bottleneck machines drive the schedules of non-bottleneck machines; comparative rankings of all the heuristics developed in the course.
Department of Electrical Engineering
Name of the PI- Prof. Nishchal Verma Abstract- Intelligent Health Monitoring of Machines are becoming an integral part of many industries contributing to higher productivity. The course covers a wide range of related topics starting from the overview of existing maintenance techniques to the development of real time intelligent fault diagnosis system. This includes salient position finding for sensor placements, data acquisition, preprocessing, feature extraction, feature selection, classification/recognition methodology. A part of the course also focusses on practical implementation through integration of smartphones and diagnostic tools for real time health monitoring of the system. The demonstrations and programming exercises have also been included for better illustrations.
Name of the PI- Prof. Nishchal Verma Abstract- Computational Intelligent techniques represent enabling technologies for the design of innovative intelligent systems for industrial control and service oriented applications. The course module brings out the motivation and increasing use of these techniques due to their performance, their capabilities in fusing noisy or incomplete data obtained from heterogeneous sensors, and the ability in adapting to variations in the operational conditions. The course focusses on the study of architecture, development and the use of state-of-the-art techniques such as Deep learning in several applications. The course contents include stacked autoencoder approach for feature selection, convolutional neural network, recurrent neural network and deep belief network architectures. The implementation of deep learning in practical problems have been lucidly shown through case studies from various sectors such as fault diagnosis in machines, feature generation for business intelligence and tumor type prediction.
Name of the PI- Prof. Nishchal Verma Abstract- Vision based Inventory Control provides user friendly environment for managing the inventory by counting multiple items placed in stock. Computer Vision based inventory control helps in counting and in maintaining the stock online and real time database of all the intended items to avoid tedious and time consuming efforts in an industry by automatic notification through email. This course mainly deals with the real time monitoring of inventory/stock using computer vision, automatic object replenishment notification to avoid stock out condition in order to improve the factors like quality, safety, efficiency, cost, customer service etc. to increase overall productivity of an industry. The course also shows the real time implementation using a desktop application for automation developed indigenously in the laboratory at IIT Kanpur, by embedding some proposed algorithms of object recognition using computer vision.
Name of the PI- Prof. Nandini gupta Abstract- Electrical Insulation is the backbone of all modern power system networks. A thorough knowledge of the fundamental properties of the materials and their failure mechanisms during service, is essential for appropriate and optimal design. In the current competitive market scenario, high voltage insulation technology has undergone many changes, with advances being made in the area of testing, measurement and development of new materials. This course is designed to acquaint students with the emerging face of insulation technology.
Name of the PI- Prof. Nandini Gupta Abstract- Accurate computation of electric, magnetic and electromagnetic fields has gained importance in recent times, with the necessity of cost-effective high-end designs in all aspects of electrical engineering. The design of equipment to minimize losses, achieve compaction, or maximize utilization of material, frequently requires a sound knowledge of the electric and magnetic field configurations involved. This course aims to teach the foundations of the Finite Element Method, and how to apply the technique for accurate electric and magnetic field computations.
Name of the PI- Prof. Nandini Gupta Abstract- In the current competitive market scenario, transmission at extra high voltages and operation of equipment at close to their design limits have necessitated strict design criteria and high testing standards. Continuous monitoring of assets and life estimation has become of paramount importance. As a result, advances have been made in the area of testing, measurement and development of new materials, and new insulation systems. In the Indian context, utilities are rapidly moving towards adopting sophisticated techniques that include on-line and off-line condition monitoring, partial discharge testing, dielectric spectroscopy etc. Researchers, in their quest for new designs and insulating materials, have resorted to techniques like space charge mapping, or optical measurements.
Department of Mechanical Engineering
Name of the faculty: Prof. Avinash Kumar Agarwal Course duration: 5 days Interested Industry: Automotive Industry
Scope of the Course
Name of the faculty: Prof. Avinash Kumar Agarwal Course duration: 5 days Interested Industry: Automotive Industry
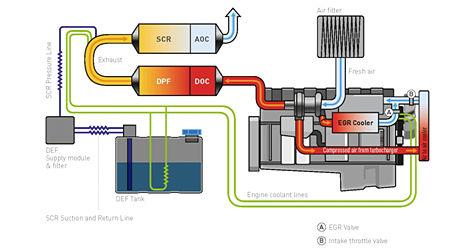
With increasing environmental awareness worldwide, stringent regulations for fuel consumption, and exhaust emissions, including those for Particulate Matter (PM) and oxides of Nitrogen (NOx) are evolving. Under these circumstances, diesel engines would continue to be attractive because of their low fuel consumption and high power output however they have to emerge as clean primary power sources also. Therefore controlling the total cost of sub-systems that lower diesel exhaust emissions become a critical issue.
Name of the faculty: Prof. Avinash Kumar Agarwal Course duration: 5 days Interested Industry: Automotive Industry
Stringent emission regulations forced researchers to innovate new technologies for better fuel consumption and reduction in exhaust emissions. Diesel and Gasoline engines would continue to be attractive because of their low fuel consumption and high power output however they have to emerge as clean primary power sources also. Therefore controlling the total cost of sub-systems that lower diesel and gasoline exhaust emissions become a critical issue. Controlling exhaust emissions at a low cost requires a sophisticated system with precise fuel injection control, corrective control using various sensors, and air management that controls combustion temperature in order to control raw emissions, along with simple after treatment methods. To realize these complex control strategies, highly sophisticated electronic solutions and micro-processor-based research and developments are necessary. In this context, It is really important to develop effective Gasoline and Diesel Engine Management Systems (EMS) capable of reduction of emissions.
Gasoline Engine Management:Cylinder charge control systems, Fuels supply, Manifold fuel injection, Gasoline direct injection, Operation of gasoline engine on natural gas, Ignition system, Inductive ignition systems, Ignition coils, Spark plugs, Sensors: Temperature sensors, Engine speed sensors, Hall effect phase sensors, Hot film air mass sensors, Piezoelectric knock sensor, Micromechanical pressure sensor, High pressure sensor, Two step lambda sensor, Electronic control unit, Operating conditions, Design and data processing.
Name of the faculty: Prof. Avinash Kumar Agarwal Course duration: 5 days Interested Industry: Automotive Industry
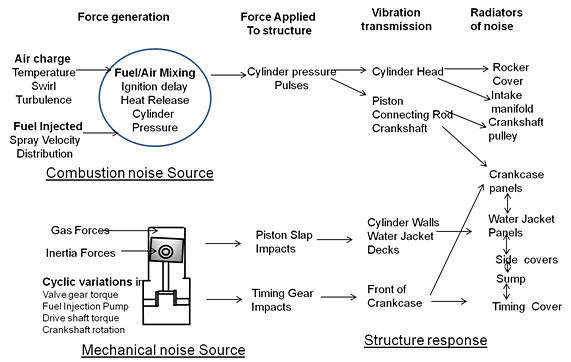
Noise generation mechanism in an engine
Name of the faculty: Prof. Avinash Kumar Agarwal Course duration: 5 days Interested Industry: Automotive Industry
To satisfy the strict emission regulations, environmental friendly alternative fuels like biodiesel for diesel engine and alcohol based fuels for gasoline engines gain popularity in last decade. However, It has a significant importance to investigate the spray and combustion characteristics of this alternative fuels because performance and emissions from the engines are largely dependent on air-fuel mixing process. Different optical diagnostic techniques such as particle image velocimetry (PIV), phase Doppler interferometry (PDI), spray and combustion visualization and endoscopy give important information of important spray and combustion parameters.
Name of the faculty: Prof. Avinash Kumar Agarwal Course duration: 5 days Interested Industry: Automotive Industry
Optimum utilization of limited resources together with control of pollutant and greenhouse-gas emissions requires sustained improvement of combustion technology. This task can be satisfied only with detailed knowledge of the underlying physical and chemical processes. Non-intrusive laser diagnostics contribute to our growing understanding of this complex and coupled multi-scale processes of combustion. Fuel-air mixing and combustion are mainly affected by in-cylinder air flow and fuel spray. Air-flow structures developed inside the engine combustion chamber significantly influence the fuel-air mixing process. Fuel spray characteristics could be determined using PDI, which provides information about droplet size distribution and 3D-velocity distributions. Spray and combustion visualization can be measured in internal combustion engine and constant volume combustion chamber (CVCC) to know soot distribution.
Optical investigation in Constant volume combustion chamber (CVCC), Laser Diagnostic techniques for spray and combustion measurement, Macroscopic spray characterization, Spray break up length, Spray tip penetration, Spray cone angle, Microscopic spray characterization, Phase doppler interferometry (PDI) measurement for fuel spray and droplet size distribution, Effects of injection pressure variation in droplet size and velocity, Introduction to optical diagnostics, Air-flow characterization, Application of spray parameters in IC engines, Air-flow characterization techniques, Particle imagine velocimetry (PIV), PIV configurations, Application of PIV, Application of optical diagnostic in engines, Combustion temperature, Ignition delay and combustion duration, Flame propagation and flame velocity in SI engines, Combustion visualization, Optical research engine, Engine endoscopy, Application of engine endoscopy in engines, Combustion visualization in combustion chamber Particle imaging velocimetry applied to engine combustion chamber, Use of single cylinder Optical Research Engine (SCORE) for engine development, Challenges for in-cylinder measurement of droplet size and velocity, High speed imaging of in-cylinder spray and combustion, Endoscopy measurement for in-cylinder combustion in engine.
Name of the PI- Prof. Sanatanu De Abstract- Combustion is still the world's dominant energy conversion technology. Fundamental knowledge of combustion is expected to improve the design of the industrial combustion systems by enhancing the flame stability, improving the combustion efficiency, and reduction in pollutant formation. This course will enable engineers and research specialists with prior knowledge of fluid mechanics, thermodynamics and computational fluid dynamics to move to an integrated understanding of theoretical and numerical aspects of combustion especially in the field of unsteady turbu-lent combustion. It will present basic techniques and recent progress in the field of numerical combustion while estab-lishing important connections with the underlying combustion basics. Further, it will present and explore examples of turbulent combustion in real combustors. The course will broadly cover general introduction to turbulence, review of existing turbulence models: RANS, LES, DNS, simple closure of chemical source terms, mixture fraction based modeling of turbulent nonpremixed combustion: flamelet model and CMC method, PDF and Monte Carlo methods, scalar mixing models, modelling of turbulent premixed flames, droplet and spray combustion.
Name of the PI- Prof. Sanatanu De Abstract- Gas turbines are used for aircraft propulsion and standalone power generation systems. On successful completion, students will be able to describe the basic principles of propulsion systems and their design and operation, relate the design of propulsion system components to the overall system performance, and critically analyse the performance of various types of propulsive units fitted to aircraft and power generation systems. The course will cover brief reviews of thermodynamics and compressible flows, basic principles of propulsion, air craft gas turbine engines: turbojet, turbofan, turboprop and ramjet, parametric cycle analysis of ideal and real engines, equations of motion in rotating coordinate system, centrifugal compressors, axial flow compressor, axial and radial turbines, combustion systems, air intake and nozzle for propulsion systems, component and engine performance analysis, application of CFD in analysis and design of turbomachinery.
Name of the PI- Prof. Sanatanu De Abstract- Combustion is still the world's dominant energy conversion technology. Fundamental knowledge of combustion is expected to improve the design of the industrial combustion systems by enhancing the flame stability, improving the combustion efficiency, and reduction in pollutant formation. This course will enable engineers and research specialists with knowledge of fluid mechanics and thermodynamics to learn fundamentals of combustion. The course will cover aspects on combustion thermodynamics, chemical equilibrium, chemical kinetics, mass transfer, conservation equations and transport properties, laminar premixed and nonpremixed flames, ignition, quenching, flammability limits and stability, droplet combustion, flame liftoff and blowout phenomena, flame stabilization in turbulent flows, and soot and NOx formation.
Name of the PI- Prof. Sameer Khandekar Abstract- Several critical components for thermal management of high power electronics and other heat dissipating components rely on liquid-vapor phase change phenomena, such as boiling, condensation and evaporation. Moreover industry prefers passive systems, requiring no external power to drive the heat transfer mechanism. Heat transfer coefficients are not only an order of magnitude greater than conventional single-phase cooling technology; the passive nature of the technology makes it very reliable. This course will cover the thermodynamic fundamentals related to phase-change phenomena and then will highlight the transport mechanisms and limitations of liquid-vapor exchange process. Case studies involving design of boilers, condensers, thermosyphons and heat pipes will be discussed.
Name of the PI- Prof. Sameer Khandekar Abstract- This course will focus on the transport mechanisms of heat transfer ranging from natural convection to single-phase and two-phase forced convection. The physical phenomena and relevant design procedure for several industrial thermal systems (Boilers, Heat-Exchangers, Condensers, Solar thermal Systems, Heat Pipes, Air-Compressors, Finned Systems, ) will be taken up. In addition, the course will also include standard testing and measurement systems and their protocols for temperature, pressure and velocity measurements.
Name of the PI- Prof. Arun Saha Abstract- The primary objective of the course is to teach fundamentals of computational method for solving linear and non-linear partial differential equations (PDE). The course offers introductory concepts about solving PDE mainly in the finite difference (FD) framework though introduction of some amount of finite volume (FV) concept is also possible.
Name of the PI- Prof. Arun Saha Abstract- The primary objective of the course is to teach both laminar and turbulent convective heat transfer. Since the adoption of general methods of approach, the students learn the concepts of mass, momentum, and energy transports leading to the understanding of hydro-thermo-diffusive structure of both internal and external flow that are of central significance to the understanding of transport processes in many technological applications.
Name of the PI- Prof. Arvind Kumar Abstract- The main objective of this course is to acquaint the participants with the concept of Additive Manufacturing (AM), various AM technologies, selection of materials for AM, modelling of AM processes, and their applications in various fields. The course will also cover AM process plan including building strategies and post-processing. This course will help industries in aviation, automotive, tooling, biomedical, rapid prototyping and 3D printing sectors to keep up with the global changes and challenges.
Name of the PI- Prof. Arvind Kumar Abstract- The objective of this course is to underline fundamentals of the casting process in order to predict and control casting defects such as segregation, shrinkage, porosity, mold filling and other heat transfer related defects. The course focuses on developing analytical and mathematical understanding of the casting and solidification process, mathematical and numerical tools for predicting the process dynamics, the associated defects, and design and control strategies. The course will also cover case studies of some advanced casting processes – direct chill casting, ingot casting, directional solidification, and multiphysics casting processes involving magnetic fields. Casting and foundry industries, automotive sector, steel and light weight casting sector will benefit from this course.
Name of the PI- Prof. Arvind Kumar Abstract- The objective of this course is to educate the participants with modelling of thermal transport involved in manufacturing processes. The focus will be on developing a feel about the physical processes, its mathematical description and numerical modelling. During introductory part on heat transfer in manufacturing, the basic of multimode heat transfer (conduction, convection and radiation), diffusive and convective heat and mass transport, natural convection and phase change will be covered. Thereafter, FDM/FVM based numerical modelling will be introduced which will involve model building, governing differential equations, numerical implementation, simulations, analysis of results etc. Case studies with in-depth study of thermal transport in selected manufacturing processes will be in the area of heat assisted manufacturing processes, casting, welding, thermal deposition, laser assisted manufacturing, additive manufacturing and machining.
Name of the PI- Prof. Arvind Kumar Abstract- Thermal energy storage systems (TESs) is a future energy technology that is attracting increasing interest for energy applications, such as space and water heating, cooling and air conditioning, waste heat recover, and many more. TES systems have enormous potential as thermal battery to facilitate more effective use of thermal equipment, renewable energy sources and large-scale energy substitutions that are economic. This course will address general aspects of thermodynamics, fluid flow, and heat transfer to the participants with background information that is of relevance to the analysis of TESs and their applications. It also includes the many types of energy storage phase change materials (PCM), material based technologies available and its several environmental issues. During this course we delves into both sensible and latent TES systems and their modelling, simulation, and numerical analyses; case studies and illustrative examples. This comprehensive course will help in providing new understanding, methodologies, models, and applications with their technical features and potential benefits; and thereby seeks to provide solutions on the future of thermal energy storage.
Name of the PI- Prof. Mohit Law Abstract- Machine tool performance and productivity is fundamentally limited by machining process induced vibrations. When these vibrations become unstable, i.e. when the machine tool system chatters, the chatter vibrations can damage the workpiece, break the tool, damage the spindle and its bearing, and also damage the machine itself. To avoid such vibrations, machine tools are often operated conservatively, resulting in underutilization of such high-value assets by a factor of two or more. This underutilization results in huge economic losses to all industries that use machines to make products. To fully harness a machine's capacity it becomes imperative to employ technologies that enable better resource utilization. This programme is geared towards introducing technologies that make possible higher utilization of machine tools. The programme will introduce the essentials of: machining process mechanics, machine tool dynamics, and of process-machine interactions to predict and avoid unstable chatter vibrations. These new ideas will enable participants to optimize their machining processes, and will also enable participants to design more productive high-performance machines and tools. Hands-on experimental testing of machine dynamics and chatter detection and avoidance will enable the participants to improve their understanding of this highly technical and non-intuitive field.
Name of the PI- Prof. Bishakh Bhattacharya Abstract- The course is primarily intended for design engineers in the mechanical, civil, electrical and aeronautical engineering industries. The course will provide these engineers with alternative design solutions for applications with challenging space, power and bandwidth constraints. Smart Materials are being developed since last decade in the laboratories all around the world. These are materials which are capable of generating controllable response to the environment. As actuators, they can produce controllable force to modify the response of a system. As sensors, the same material could be used to monitor the response of the system. Tailoring the gamut of smart materials towards diverse applications in the field of Aerospace, Civil, Mechanical and Biomedical technology is still a major challenge to the researchers and engineers involved in these fields. The objective of the short course is to familiarize people with different classes of ceramic and polymeric smart materials; development of actuators and sensors and their integration into a smart structure.
Name of the PI- Prof. Bishakh Bhattacharya Abstract- Intelligent Health Monitoring of machines has been defined and discussed extensively in the last two decades due to enormous advancements in smart material based sensing technology. In a broad sense, this refers to the implementation of a sensing strategy based on distributed smart sensors with four sequential objectives: (a) Detect the presence of damage, if affirmative then (b) Find out the location of damage, (c) Estimate the extent of damage and finally (d) Interpret the nature of damage and estimate the remaining useful life. In this course, we will first discuss about the basic axioms of structural health monitoring. Subsequently, we will provide a brief review of smarts sensors. We will then focus on health monitoring for reduction of vibration and performance enhancements of machine elements. This will be followed by discussions on various Damage Criteria. Finally, we will discuss about multi-sensor data fusion, active self-healing and structural health management. A case study will be considered with respect to pipe-line health monitoring.
Name of the PI- Prof. Bishakh Bhattacharya Abstract- This intensive course aims at providing an holistic approach to product design. We will start with introductory notes on Product Design covering various kinds of product design, team building and phases of product design. This will be followed by materials selection for mechanical design based on Ashby Diagrams. Next we will focus on concept generation: Axiomatic Design and Theory of Inventive Problem Solving (TRIZ) will be covered in this phase. We will then discuss about the future of product design: the application of Artificial Intelligence, Data Driven Optimization and Embedded Intelligence. Lastly we will take up some case studies on each of the topics which includes material selection for machine components and structural elements, application of TRIZ and Axiomatic Design for New Product Development.
Department of Economic Sciences
Name of the PI- Prof. Deep Mukherjee Abstract- This is an introductory course (3/4 days) that assumes no prior knowledge of economics but some knowledge of high school algebra is required. The course has four main components: (i) consumer behavior; (ii) producer behavior; (iii) market models; and (iv) project appraisal. The following concepts/topics will be covered: consumer preferences, a consumer's optimum choice, demand function, price index number, production function, returns to scale, short run and long run costs, behavior of profit maximizing firms, perfect competition, monopoly, duopoly, government intervention in terms of tax and subsidy, and cost benefit analysis.
Name of the PI- Prof. Deep Mukherjee Abstract- This is an introductory course (4/5 days) that assumes no prior knowledge of statistics but some knowledge of high school algebra, calculus, and excel spreadsheet is required. The course has four main components: (i) descriptive statistics; (ii) probability and random variables; (iii) linear regression model; and (iv) estimation of demand, production, and cost functions. The following concepts/topics will be covered: graphical and numerical summary to describe the distribution of a variable, relationship between two variables (correlation), basic probability theory, expectation and variance of a random variable, common distributions (binomial, normal), hypothesis testing, and classical linear regression model. A brief introduction to will be given on demand function and cost function estimations using real life data. This course will also cover statistical data analysis using excel spreadsheet.
Name of the PI- Prof. Somesh Mathur
Course number: ECO 524
Name of the PI- Prof. Somesh Mathur Abstract- This course is meant for senior undergraduate students who need to learn about panel data procedures and its applications with knowledge on advances in methodological panel data procedures by utilizing standard econometric softwares. Panel data models account for the unobserved heterogeneity terms not accounted sometimes in the regression model. GMM(Generalized Method of Moments) and IV(Instrumental Variable) procedures are used to account for lagged dependent term on the right hand side of the regression model in a dynamic panel framework. The topics that will be covered( not exhaustive) would be the Fixed Effect procedures, Pooled OLS and Random Effect Procedures, Diagnostics for choosing the above models with appropriate tests like Hausman test, Tests for Heteroscedasticity and Autocorrelation in panel framework, Dynamic Panel Data Models, Estimation Procedures like GMM to estimate Dynamic Panel data Models, Panel Unit Root tests, Cointegration and Panel VAR Models( with interpretations) and Panel Models with Limited Dependent Variable responses, application of Panel data in Trade, Finance, Industrial Economics, Macroeconomics and Microeconomics, among others with hands on experience of doing panel data analysis through standard econometric softwares. Panel data is now being increasingly used in universities and institutes of higher learning, by students, and researchers, policy makers, academia, among others, generally, with the availability of unit level, individuals and firm level data for number of years. Course Content (Number of Lectures are in the Parenthesis):
Total Number of Lectures: 42 Department: Economic Sciences
Name of the PI- Prof. Somesh Mathur Abstract- Objectives of the Course: This is the second level course in Econometrics, offered to the post graduate students of the economics discipline of the HSS, who are now following a new PG template since 2015(I).The focus will be on advanced econometric models, new data sets, and various estimation procedures keeping applied economics in mind. This course would give hands on experience to students working on various data sets using R, and other econometric software like Eviews and Stata. Lab sessions would be inherent part of the course. Course Content: Non Linear Regression Models, Non Parametric Regression Models, Measurement Errors, Stochastic Regressor, Multinomial and Conditional Logit Models, Ordered Logit Models, Nested Logit Models, Random Parameter Models, Truncation, Censoring and Sample Selection Models, Duration and Event Count Models, Dynamic Panel Data Models, Time Series Models including ARCH,GARCH and Multivariate GARCH Models, DEA and Stochastic Frontier Models, Total Factor Productivity Estimation, Levinsohn Petrin Approach of Measurement of Productivity, Single and Multiple Equation GMM Procedures, Spatial Regression Models and its applications, Application of Econometric Models to Trade, Finance, Microeconomics, Development Economics, Growth, Macroeconomics, Industry, among others. Lecture-wise Break-up (Each Lecture is of 50 Minutes Duration):
References and Textbooks
Department: Economics Sciences, IIT Kanpur
Name of the PI- Prof. Somesh Mathur Duration- 5 Days Abstract- Global Trade and Empirical Facts of International Trade; Nature of the Globalization Process and Benefits and Costs associated with the Globalization Process, Globalization and Wages; Theory and Empirical Testing of Trade Theories; Alternative Trade Theories and their Empirical Tests; Relationship between Trade ,Economic Geography and Agglomeration economies ,Political Economy of Trade Policy; Gains from Trade and the impact of trade on income distribution, trade patterns of developing countries and development issues, Stopler-Samuelson Theorem and Rybczynski Theorem; Instruments of Trade Policy and Welfare Effects; Nominal and Effective Rate of Protection, Optimum tariff, Lerner and Metzler Paradox; International Factor Movements including the impact and spill over effects of FDI and Portfolio Investments ;Different forms of Economic Integration and benefits and costs associated with it; Trade, Technology and Growth,; Trade, Exchange Rate and Balance of Payments, Exchange rate management including hedging, different models of currency and banking crises and empirical assessment of BOP crises, international monetary theories and policies and macroeconomic management of an open economy Trade Policy simulations using software like GTAP and GAMS, International Trade Data Analysis using Econometric Models, introduction to WITS data base; WTO negotiations and Issues like TRIPS, GATS, trade and environment and labour standards, Dispute Settlement Process of the WTO, NAMA, among others.
Name of the PI- Prof. Somesh Mathur Specialized Infrastructure requirement: In addition to the lectures, the students would be exposed to some databases, and statistical and econometric software, keeping hands-on experience of students in mind. The major databases and software needed are: Prowess, World Bank World Development Indicators (on CDRom), Global Competitiveness Report Database, CSO's NSS Database, Eviews, Stata, Limdep, Matlab, among others. Instructional aspects: The students may be asked to write a short-term empirical research paper, using (a) data from various databases, (b) various statistical and econometric software, and (c) knowledge of some computing language codes. Course content: (This will go in the "Courses of Study" book. Please note that the duration of each lecture is 50 minutes.) Non Linear Regression Models, Non Parametric Regression Models, Measurement Errors, Stochastic Regressor, Multinomial and Conditional Logit Models, Ordered Logit Models, Nested Logit Models, Random Parameter Models, Truncation, Censoring and Sample Selection Models, Duration and Event Count Models, Dynamic Panel Data Models, Time Series Models including ARCH,GARCH and Multivariate GARCH Models, DEA and Stochastic Frontier Models, Total Factor Productivity Estimation, Levinsohn Petrin Approach of Measurement of Productivity, Single and Multiple Equation GMM Procedures, Application of Econometric Models to Trade, Finance, Microeconomics, Development Economics, Growth, Macroeconomics, Industry, among others. Lecture-wise break-up: (please note that the duration of each lecture is 50 minutes)
Suggested Text and Reference Material:
Department of Chemical Engineering
Name of the PI- Prof. Animangsu Ghatak Abstract- PSAs are used in wide ranging applications, as in adhesive tapes of various kinds, transdermal patches, easy release coatings, sealants and so on. In these different applications it is required to know the basic physics of adhesion, e.g. the effect of rheological characteristics of the adhesive material, its thickness, nature of intermolecular interaction at the interface and even the effect of substrate physical and chemical properties. We will cover the following topics: basic elasticity equations; deformation of an elastic film sandwiched between two parallel plates; theory of contact mechanics of elastic half space; Hertzian mechanics; JKR mechanics, deformation of thin flexible plate; Analysis of peel adhesion tests; Adhesion on patterned substrates.
|
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||